Whiplash is a class of neck injury sustained by or linked to an abrupt neck displacement.Whiplash, also known as whiplash-associated disorder (WAD), is frequently caused by being struck from behind, such as by a fast-moving car in an automobile accident.When a hit is given, the individual's body is forced forward, but their head stays behind for a short instant. It causes the head to move up and down, straining and occasionally injuring muscles, tendons, and ligaments.Most whiplash patients recover within two to three weeks by maintaining a treatment regimen that combines pain medication and exercise. Some patients, however, experience persistent neck discomfort and other long-term problems.In this article, we can see what Whiplash is, what it causes, its symptoms, how it is diagnosed, and how to treat Whiplash. Whether you've recently been in an accident or are curious about this type of injury, this post will provide valuable information about whiplash symptoms.Read Also: Neck Stretches for Instant Relief from Pinched Nerve Pain Whiplash happens when a person's head suddenly goes forward and backward with high power. The injury is more prevalent after a rear-end accident. Whiplash occurs when the neck's soft tissues (muscles and ligaments) extend beyond their normal range of motion. Because the symptoms may not present for a while, monitoring physical differences for many days following any collision or other injury incident is critical.Whiplash is considered a minor ailment, but it may bring long-term pain and suffering.Read Also: 15 Best Pain Relief Gels
Whiplash happens when a person's head suddenly goes forward and backward with high power. The injury is more prevalent after a rear-end accident. Whiplash occurs when the neck's soft tissues (muscles and ligaments) extend beyond their normal range of motion. Because the symptoms may not present for a while, monitoring physical differences for many days following any collision or other injury incident is critical.Whiplash is considered a minor ailment, but it may bring long-term pain and suffering.Read Also: 15 Best Pain Relief Gels Whiplash symptoms vary depending on the severity and how badly the neck is dislocated or compressed. The more extension or compression there is, the more severe the damage.The timing of whiplash symptoms is critical. Some of the symptoms of whiplash emerge shortly after a collision, whereas others require a minimum of 12 hours. It may take a whole day or a few days for all symptoms to manifest.Because Whiplash may have various consequences, doctors developed a grading scale for the intensity of whiplash-related diseases. This grading system is known as the Quebec Classification of Whiplash-Associated Illnesses.The grading system is listed below:Grade 0: No injuries.Grade 1: Only pain.Grade 2: Pain and symptoms of damage.Grade 3: Pain and evidence of damage and neurological repercussions.Grade 4: Extreme pain and evidence of major or dangerous neurological consequences.
Whiplash symptoms vary depending on the severity and how badly the neck is dislocated or compressed. The more extension or compression there is, the more severe the damage.The timing of whiplash symptoms is critical. Some of the symptoms of whiplash emerge shortly after a collision, whereas others require a minimum of 12 hours. It may take a whole day or a few days for all symptoms to manifest.Because Whiplash may have various consequences, doctors developed a grading scale for the intensity of whiplash-related diseases. This grading system is known as the Quebec Classification of Whiplash-Associated Illnesses.The grading system is listed below:Grade 0: No injuries.Grade 1: Only pain.Grade 2: Pain and symptoms of damage.Grade 3: Pain and evidence of damage and neurological repercussions.Grade 4: Extreme pain and evidence of major or dangerous neurological consequences.
What is Whiplash?
 Whiplash happens when a person's head suddenly goes forward and backward with high power. The injury is more prevalent after a rear-end accident. Whiplash occurs when the neck's soft tissues (muscles and ligaments) extend beyond their normal range of motion. Because the symptoms may not present for a while, monitoring physical differences for many days following any collision or other injury incident is critical.Whiplash is considered a minor ailment, but it may bring long-term pain and suffering.Read Also: 15 Best Pain Relief Gels
Whiplash happens when a person's head suddenly goes forward and backward with high power. The injury is more prevalent after a rear-end accident. Whiplash occurs when the neck's soft tissues (muscles and ligaments) extend beyond their normal range of motion. Because the symptoms may not present for a while, monitoring physical differences for many days following any collision or other injury incident is critical.Whiplash is considered a minor ailment, but it may bring long-term pain and suffering.Read Also: 15 Best Pain Relief GelsWhat are the whiplash symptoms?
 Whiplash symptoms vary depending on the severity and how badly the neck is dislocated or compressed. The more extension or compression there is, the more severe the damage.The timing of whiplash symptoms is critical. Some of the symptoms of whiplash emerge shortly after a collision, whereas others require a minimum of 12 hours. It may take a whole day or a few days for all symptoms to manifest.Because Whiplash may have various consequences, doctors developed a grading scale for the intensity of whiplash-related diseases. This grading system is known as the Quebec Classification of Whiplash-Associated Illnesses.The grading system is listed below:Grade 0: No injuries.Grade 1: Only pain.Grade 2: Pain and symptoms of damage.Grade 3: Pain and evidence of damage and neurological repercussions.Grade 4: Extreme pain and evidence of major or dangerous neurological consequences.
Whiplash symptoms vary depending on the severity and how badly the neck is dislocated or compressed. The more extension or compression there is, the more severe the damage.The timing of whiplash symptoms is critical. Some of the symptoms of whiplash emerge shortly after a collision, whereas others require a minimum of 12 hours. It may take a whole day or a few days for all symptoms to manifest.Because Whiplash may have various consequences, doctors developed a grading scale for the intensity of whiplash-related diseases. This grading system is known as the Quebec Classification of Whiplash-Associated Illnesses.The grading system is listed below:Grade 0: No injuries.Grade 1: Only pain.Grade 2: Pain and symptoms of damage.Grade 3: Pain and evidence of damage and neurological repercussions.Grade 4: Extreme pain and evidence of major or dangerous neurological consequences.Grade 0 -
An individual with Whiplash does not experience pain or display other symptoms or indications of damage at this level.Grade 1 -
This is the initial degree of Whiplash when a person experiences pain. They will also indicate the following:- Stiffness when moving.
- Tenderness to touch in the region of the injury.
Grade 2 -
The initial level at which a person exhibits pain, other Grade 1 symptoms, and visible symptoms of an injury. The discomfort might also have different consequences than in Grade 1.Grade 2 whiplash symptoms include the following.- The pain spreads to surrounding regions such as the face, head, shoulder, and back.
- Muscular spasms make it difficult to move or turn the head and neck.
- Injury symptoms include swelling, bruising, and sensitivity to touching at the area of the injury.
Grade 3 -
Grade 3 whiplash includes neurological problems. They occur when swelling or inflammation interrupts nerve impulses moving to or from the brain through the affected location.These are some of the symptoms:- Muscular weakness.
- Numbness (lack of sensation for warmth, cold, or pain) in the neck, upper back, shoulder, or upper arms.
- Paresthesia (burning, tingling, or "pins and needles" sensation) in the neck, back muscles, shoulders, or upper arms.
- Headaches.
- Vision issues.
- A sensation of movement or spinning (vertigo).
- Ringing in one's ears (tinnitus).
- Sleep disturbances.
Grade 4 -
This is the most severe level of whiplash-related problems. They often include all preceding symptoms, particularly neurological ones, but are more severe. As neurological symptoms become more severe, it may indicate that at least 1 neck vertebra has fractured, is misplaced, or is moving out of position, placing pressure on the spinal cord or adjacent nerves.These are some of the rare symptoms of Whiplash:- Irritability.
- Memory lapse.
- Inability to concentrate.
What are the causes of Whiplash?
Whiplash happens when the neck muscles are strained due to a sudden backward and forward movement. Tendons and ligaments in the neck strain and tear result from the abrupt action.In trying to compensate for the rapid movement, the muscles typically pull the head back too strongly, further overstretching in the reverse direction.The jolt (or hit to the head) might originate from the back, the front, or the side. Even a little incident might result in Whiplash.The following are some of the most popular incidents or activities that might cause Whiplash:Automobile incidents. Rear-end crashes commonly cause Whiplash.Assault or physical abuse. Whiplash can develop as a result of being hit or shaken. One of the injuries associated with shaken baby syndrome.Sports involve physical contact. Football collisions and other sports-related incidents can occasionally result in Whiplash.How is Whiplash diagnosed?
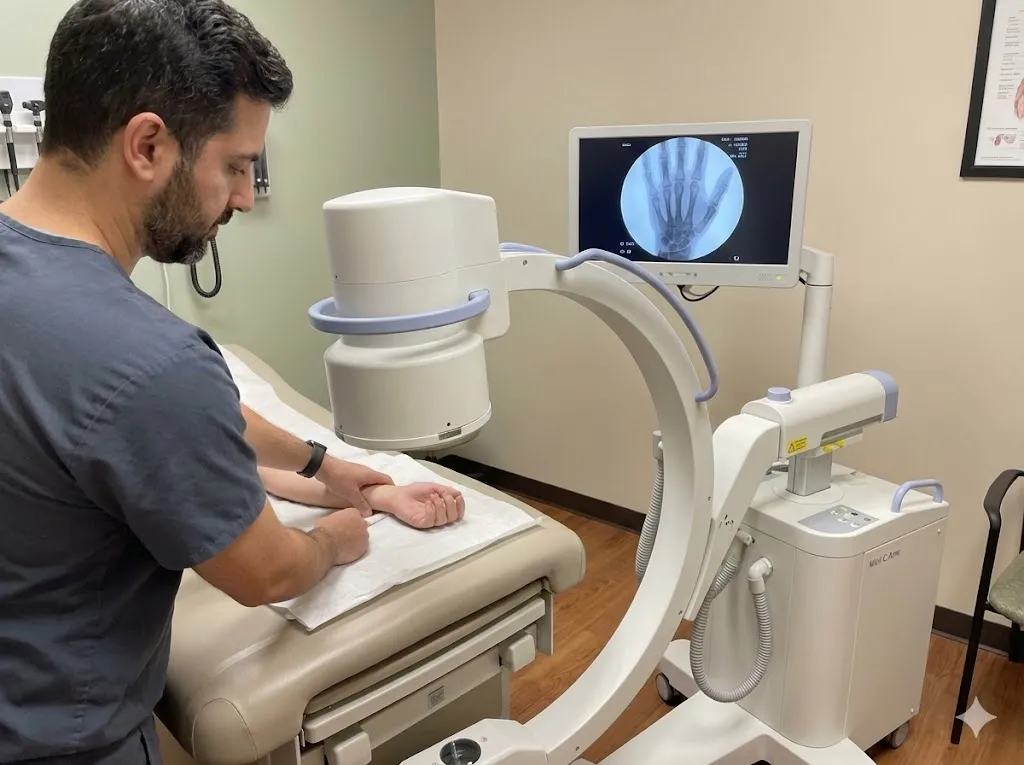
The person will be examined by the doctor, who will check for any recent accidents, athletic events, falls, or hits to the head.When a spinal injury is diagnosed, the following imaging studies may be ordered:- X-rays can rule out fractured bones and other disorders such as spinal fractures, arthritis, and dislocations.
- CT (computerized tomography) scan - a series of X-ray pictures are obtained from various angles to provide a complete picture of the bones and soft tissues on display.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan - radio signals and a powerful magnetic field provide a detailed image of the afflicted region over time. The doctor will detect soft tissue damage.
What are the treatment options for Whiplash?
Certain whiplash treatments are more effective immediately following an accident, and others are most beneficial when used to address the long-term repercussions and chronic difficulties caused by a whiplash injury. Some people can accomplish both. The most frequent whiplash treatment are as follows:- Immobilization.
- Medications.
- Osteopathy.
- Collars.
- Posture.
- Injections.
- Relaxants for the muscles.
- For the initial 7 to 10 days, use cold packs. Following that, heat application is advised.
- Physical treatment and exercise.
- TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) treatment.
- Nerve ablation by radiofrequency energy.
- Spinal surgery.
Conclusion -
Whiplash can be a painful and disruptive injury that can have a significant impact on your daily life. Whiplash symptoms can vary widely, from neck pain and stiffness to headaches and dizziness, and can last for weeks or even months. If you suspect you have whiplash, it's important to seek medical attention and follow a treatment plan to manage your symptoms and promote healing. While whiplash can be challenging to recover from, there are a variety of treatment options available, including physical therapy, medication, and chiropractic care. With the right approach, you can minimize the impact of whiplash and return to your normal routine as quickly as possible. Remember to always take care of yourself and seek help if you need it.
Reviewed by