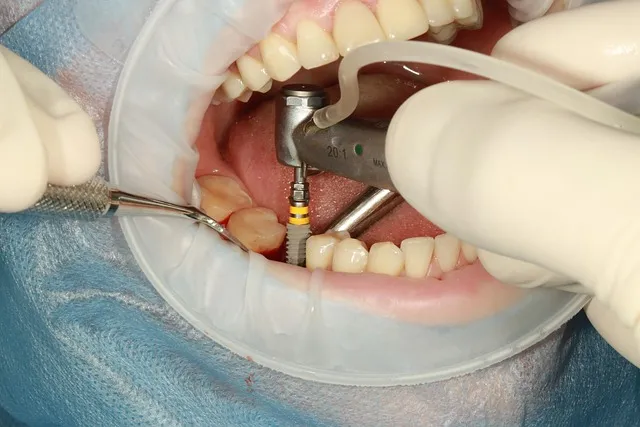
Bunions are a common foot problem that affects millions of people worldwide. They occur when the joint at the base of the big toe becomes misaligned, causing a bony bump to develop on the side of the foot. While many bunions can be managed with non-surgical treatments, some cases may require bunion surgery to correct the underlying issue.
Several types of bunion surgery are available, each with its unique approach and benefits.
This blog will help you understand the most common bunion surgery types, including traditional bunionectomy, minimally invasive bunion surgery, and joint-preserving bunion surgery.
 A bunion is an enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It can be painful and make walking difficult. Bunion surgery is performed to correct the deformity and relieve pain. Bunion surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is asleep during the procedure. The surgery usually takes 1-2 hours, although this will depend on the type of procedure being performed. After surgery, patients usually stay in the hospital for 1-2 days before being discharged home. Recovery time varies depending on the type of procedure, but patients can expect to take 4-6 weeks before fully recovering.
A bunion is an enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It can be painful and make walking difficult. Bunion surgery is performed to correct the deformity and relieve pain. Bunion surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is asleep during the procedure. The surgery usually takes 1-2 hours, although this will depend on the type of procedure being performed. After surgery, patients usually stay in the hospital for 1-2 days before being discharged home. Recovery time varies depending on the type of procedure, but patients can expect to take 4-6 weeks before fully recovering.
What is Bunion Surgery?
 A bunion is an enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It can be painful and make walking difficult. Bunion surgery is performed to correct the deformity and relieve pain. Bunion surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is asleep during the procedure. The surgery usually takes 1-2 hours, although this will depend on the type of procedure being performed. After surgery, patients usually stay in the hospital for 1-2 days before being discharged home. Recovery time varies depending on the type of procedure, but patients can expect to take 4-6 weeks before fully recovering.
A bunion is an enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It can be painful and make walking difficult. Bunion surgery is performed to correct the deformity and relieve pain. Bunion surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is asleep during the procedure. The surgery usually takes 1-2 hours, although this will depend on the type of procedure being performed. After surgery, patients usually stay in the hospital for 1-2 days before being discharged home. Recovery time varies depending on the type of procedure, but patients can expect to take 4-6 weeks before fully recovering.
When is bunion surgery performed?
Most commonly, bunion surgery is recommended for patients who experience pain daily. The pain may be caused by the deformity or shoes rubbing against the bunion. Surgery may also be recommended for patients with difficulty walking or arthritis in the foot. In some cases, bunion surgery may be performed for cosmetic reasons. Bunion surgery is not typically recommended for patients who are pregnant or who have diabetes, as these conditions can complicate recovery. Surgery is also not usually recommended for children, as the bones in their feet are still growing, and the deformity may correct itself over time. Also Read: Diabetes Swollen Feet: Causes And TreatmentsWhat are the Bunion surgery Types & Treatments?
There are several bunion surgery types available. The surgery type depends on the deformity's severity and the patient's circumstances. The most common type of bunion surgery is called a bunionectomy. This involves removing the bony bump and realigning the bones in the foot. Sometimes, part of the big toe joint may also be removed.1. Bunionectomy: Removal of the Bunion -
Purpose: To remove the bony bump (bunion) on the side of the big toe. Use: Recommended for patients with a painful bunion that is not improving with non-surgical treatments. Prevalence: Bunionectomy is a common procedure for the treatment of bunions. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 1-2 hours to complete. Recovery Time: Varies but 4-6 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, and poor wound healing are possible complications of a bunionectomy.2. Osteotomy: Repositioning of the Big Toe to Correct the Bunion -
Purpose: To realign the bones in the big toe and correct the bunion. Use: Recommended for patients with mild to moderate bunion and flexible joints. Prevalence: Osteotomy is a common procedure for the correction of bunions. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 1-2 hours to complete. Recovery Time: Varies but 4-6 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, poor wound healing, and joint stiffness are possible complications of the osteotomy. Book Appointment with the best Foot Surgery Doctors in India3. Arthrodesis: Fusion of the Joint in the Big Toe to Prevent Movement and Alleviate Pain -
Purpose: To fuse the joint in the big toe to prevent movement and alleviate pain. Use: Recommended for patients with severe bunion or joint arthritis in the big toe. Prevalence: Arthrodesis is less common than bunionectomy and osteotomy but may be recommended for severe cases of the bunion or joint arthritis. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 1-2 hours to complete. Recovery Time: Vary 6-12 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, poor wound healing, and joint stiffness are possible complications of arthrodesis.4. Lapidus Procedure: Correction of the Alignment of the Bones in the Forefoot -
Purpose: To correct the alignment of the bones in the forefoot, specifically the first metatarsal bone and the lateral cuneiform bone. Use: Recommended for patients with severe or complex bunions or other forefoot deformities. Prevalence: The Lapidus procedure is less common than bunionectomy, osteotomy, and arthrodesis but may be recommended for a severe bunion or forefoot deformity cases. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 1-2 hours to complete. Recovery Time: Vary 6-12 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, poor wound healing, and joint stiffness are possible complications of the Lapidus procedure. Book an Online Appointment with the Best Arthrodesis Foot Doctors in India5. Implant Arthroplasty: Placement of an Artificial Joint to Correct the Bunion -
Purpose: To replace the damaged joint in the big toe with an artificial joint to correct the bunion. Use: Recommended for patients with a severely arthritic joint in the big toe or not candidates for other surgical options. Prevalence: Implant arthroplasty is less common than other surgical options for bunions and is a last resort. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 1-2 hours to complete. Recovery Time: Vary 6-12 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, implant failure, and poor wound healing are possible complications of implant arthroplasty.6. Screw Fixation Osteotomy -
Purpose: To realign the bones in the big toe and correct the bunion using screws for fixation. Use: Recommended for patients with mild to moderate bunion and flexible joints. Prevalence: Screw fixation osteotomy is a less common option for correcting bunions but may be used in certain cases. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 1-2 hours to complete. Recovery Time: Varies but 4-6 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, screw failure, and poor wound healing are possible complications of screw fixation osteotomy.7. Distal Metatarsal Osteotomy -
Purpose: To realign the bones in the forefoot and correct the bunion. Use: Recommended for patients with mild to moderate bunion and flexible joints. Prevalence: Distal metatarsal osteotomy is a less common option for correcting bunions but may be used in certain cases. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 1-2 hours to complete. Recovery Time: Varies but 4-6 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, poor wound healing, and joint stiffness are possible complications of the distal metatarsal osteotomy. Also Read: Top 5 Most Likely Reasons For Foot Pain8. Proximal Phalanx Osteotomy -
Purpose: To realign the bones in the big toe and correct the bunion. Use: Recommended for patients with mild to moderate bunion and flexible joints. Prevalence: Proximal phalanx osteotomy is a less common option for correcting bunions but may be used in certain cases. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 1-2 hours to complete. Recovery Time: Varies but 4-6 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, poor wound healing, and joint stiffness are possible complications of proximal phalanx osteotomy. Contact with the best Osteotomy Foot Doctors in India9. Minimally Invasive Bunionectomy -
Purpose: To remove the bunion with smaller incisions and less disruption of surrounding tissues. Use: Recommended for patients with mild bunion and flexible joints. Prevalence: Minimally invasive bunionectomy is a newer and less invasive option for correcting bunions but may be used in certain cases. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 30 minutes to 1 hour to complete. Recovery Time: Varies but 4-6 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, poor wound healing, and joint stiffness are some possible complications of a minimally invasive bunionectomy.10. Reverse Lapidus procedure -
Purpose: To realign the bones in the forefoot and correct the bunion by repositioning the first metatarsal bone. Use: Recommended for patients with severe or complex bunions and rigid joints. Prevalence: The reverse Lapidus procedure is a less common option for correcting bunions but may be used in certain cases. Length of Procedure: Varies but takes 1-2 hours to complete. Recovery Time: Varies but 4-6 weeks of limited weight-bearing and physical therapy. Complications: Pain, swelling, infection, poor wound healing, and joint stiffness are possible complications of the reverse Lapidus procedure. Some types of Bunion surgery may involve some discomfort and inconvenience in the short term, but the long-term benefits of correcting the underlying issue can greatly improve a patient's quality of life and mobility. Also Read: Orthotics and BunionFAQS -
Conclusion -
Bunion surgery can be a highly effective treatment option for those who suffer from severe bunions that do not respond to non-surgical treatments. However, the decision to undergo bunion surgery should not be taken lightly, as it is a major medical procedure that requires careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits. All the bunion surgery types offer unique advantages and drawbacks. Patients should consult with their healthcare provider to determine which type of bunion surgery is best suited for their individual needs and circumstances. Book online appointment with the Best Bunion Doctor in India
Reviewed by