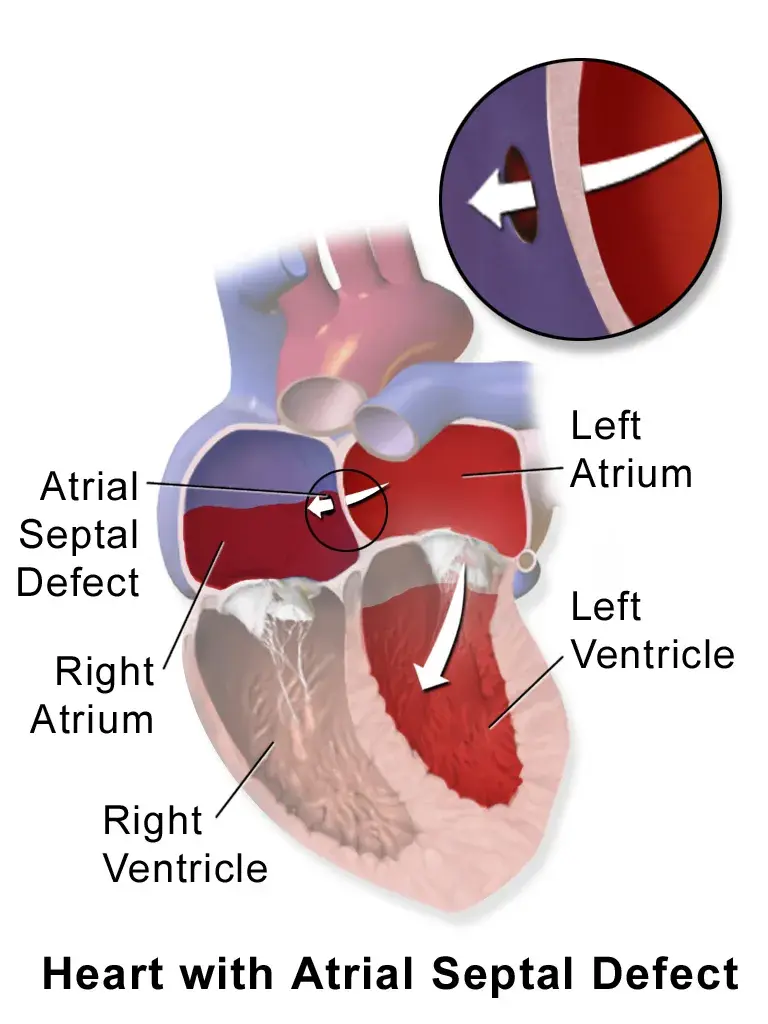
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD), commonly known as Hole in Heart, is a congenital disorder of the heart that involves a hole in the wall (septum) that divides the two upper chambers of the heart. The defect causes freshly oxygenated blood in the upper left chamber of the heart (or left atrium) to flow into the upper right chamber (right atrium) of the heart, causing mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. If the hole is large, the extra volume of blood that is pumped from the right side of the heart can lead to the following:
- The weakening of right side of the heart.
- Overfilling of lungs and overworking of heart.
- Increased blood pressure in lungs, leading to pulmonary hypertension.
What are the causes ASD?
A normal heart is divided into four chambers - two upper chambers are known as atria (and separated from each other by the atrial septum) and two lower chambers are known as ventricles (separated from each other by the ventricular septum). At birth, the two atria are connected through a small opening known as the foramen ovale, which gets sealed gradually with time through the formation of the atrial septum.
However, an atrial septal defect occurs if the atrial septum is not formed completely during fetal development or does not close the hole properly. The prolonged opening of the foramen ovale results in the excessive blood flow to the lungs and high blood pressure. As per an experienced cardiac surgeon,
The disorder takes place at about 5 weeks of pregnancy when heart development generally takes place. Genetics and environmental factors are also thought to play a role in development of the disorder. It is not possible to prevent atrial septal defects but one can take precautions and guidance on immunity, current health condition and family medical history from a health care provider if planning a pregnancy in the near future.
Congenital heart defects run in families and may have a genetic linkage with disorders like the Down's syndrome. The doctor can guide people about the chances of having children with a heart defect if they or their older children suffer from one. Further, a rubella infection and consumption of alcohol or drugs during pregnancy can harm the foetus and increase the risk of having a baby with ASD.
What are the symptoms of ASD?
A person might not show any symptoms of atrial septal defect if s/he do not suffer from any other heart defect or have a small defect (less than 5 mm), or if the symptoms develop at around 30 years of age or later.
Commonly occurring symptoms of ASD include:
- Heart murmur (whooshing sound heard through a stethoscope)
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Fatigue
- Swelling of feet, legs or abdomen
- Bluish skin color
- Stroke
How is ASD diagnosed?
A routine examination may detect abnormal heart sounds like a murmur, which is caused by turbulent flow of blood. A general practitioner will refer an affected person to a cardiologist or cardiac surgeon for further investigation of the heart. Alternatively, the affected adult or their child may visit a cardiologist if they experience any of the symptoms listed above.Based on the symptoms, physical examination and tests for the heart, the doctor will determine the size and severity of the atrial septal defect. Following tests may be conducted to diagnose ASD:
- Echocardiogram - Often the first test done for ASD, an electrocardiogram converts sound waves to video images of the heart. This allows the doctor to measure pumping strength of the heart chambers, valves and signs of heart defects.
- ECG - This method can identify heart rhythm problems by monitoring electrical activity of the heart.
- Cardiac Catheterization - The doctor can check the heart's pumping action and functioning of heart valves by inserting a catheter into a blood vessel in the groin or arm and guiding it to the heart.
- Coronary Angiography - This method is used in patients aged 35 years or more. Blood flow through the heart's arteries is determined using a special dye and x-rays.
For pregnant women, foetal echocardiography will be conducted as part of routine antenatal examinations. An ultrasound scanner creates a picture of the baby's heart, which is useful in identifying any congenital heart disease.
Read about the relationship between Pregnancy and Heart Problems
What are the treatment options for ASD?
Treatment of ASD depends on the size of the hole in an adult or a child's heart. The small defect may not require any treatment as these may close on its own during childhood. However, in cases of large septal defects, medication and surgery may be required.
- Medications - Medications do not treat the hole, but relieve some symptoms and reduce the risk of complication post-surgery. Patients may be prescribed medicines for keeping their heartbeat regular (beta blockers and digioxin) or reducing the risk of blood clots (anticoagulants like warfarin and aspirin).
-
Surgery - Surgical repair, for both children and adults, involves plugging the opening between the atria, through two methods:
- Cardiac catheterization - A plug or patch is guided through a catheter put in a blood vessel (groin) and placed at the site of the hole. Heart tissue grows around the mesh and seals it permanently.
- Open-heart surgery - Performed under general anaesthesia, the surgeon will stitch or use patches to seal the hole.
What are the known complications due to ASD?
Congenital heart diseases like ASD are prone to further problems like:
- Developmental issues in children - Delay in development, learning difficulty due to poor oxygen supply during early life that affects brain development.
- Respiratory tract infections
- Endocarditis
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Heart rhythm problem and heart failure
- Blood clots
- Sudden cardiac death
It is essential to keep one's heart healthy by taking a diet rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains, and avoiding cholesterol, saturated fats and sodium-rich foods. Persons affected by atrial septal defect can discuss the permissible level of physical activity for their condition with their doctor.
This article was reviewed by highly experienced and renowned doctors at Apollo Hospitals, Indore. Feel free to book an appointment with Cardiologists in Apollo Hospitals, Indore. About: Apollo Hospitals, Indore - Cardiology Team. The Cardiac Team at Apollo Hospitals are trained at the top institutes in India and abroad. They are completely dedicated to the prevention and treatment of numerous cardiac diseases. With over 1,50,000 cardiac cardiothoracic surgeries performed till date, it's not a surprise that the Apollo Heart Institutes are regarded as one of the top centers in the world. The team of specialists is experienced in the most complex of cases, right from complicated coronary artery bypass surgery, valvular heart disease surgery to heart surgery for children, with success rates comparable to international standards.
Reviewed by