Uterus is an important female reproductive organ. It consists of three parts - Fundus, Corpus, and the Cervix. The Uterus has two layers - Endometrium (Inner layer) and Myometrium (Outer Layer). Uterine Cancer refers to Cancers arising out of the Uterus. It is the abnormal growth of cells in the Uterus.

The most common form of Uterine Cancer is the Endometrical Cancer.
Cancer Cells originate from the Endometrium and may gradually invade the Myometrium, Cervix, Vagina, Lymph Nodes, and other parts of the body.
Types
The main types of Uterine Cancer are as follows:
- Uterine Sarcomas: This arises from the muscular layer of the Uterus
- Endometrical Cancer: This cancer originates from the glands and connective tissues of the Endometrium
- Cervical Cancer: This form of Cancer arises from the Cervix
Causes
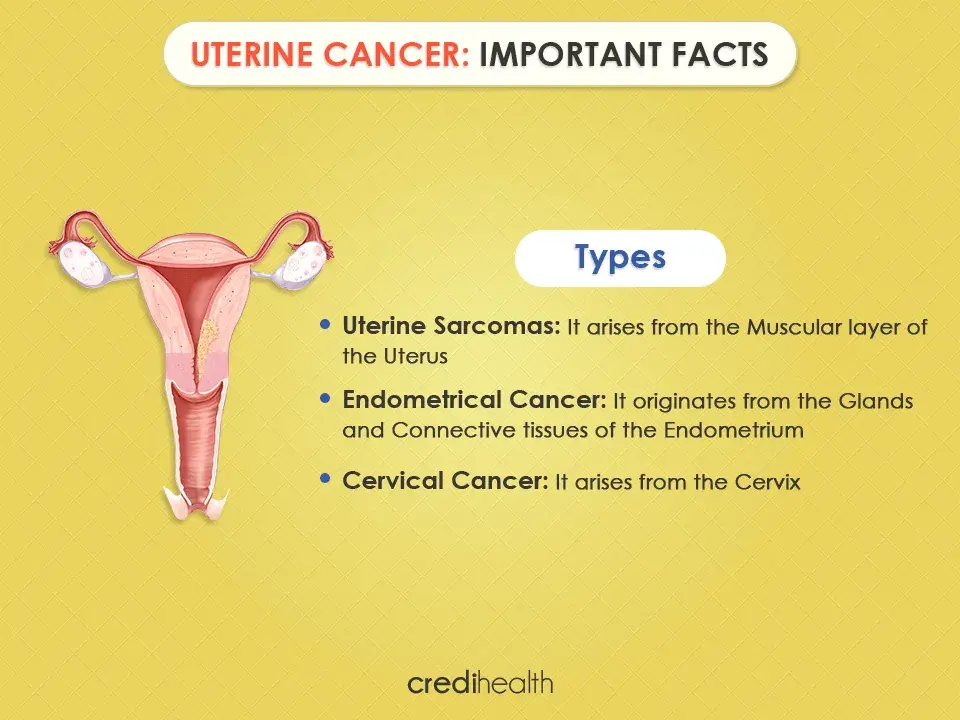
The precise causes for Uterine Cancer are still unknown. However, according to experts, there are certain risk factors which may induce occurrence of Uterine Cancer. The risk factors are as follows:
- Obesity
- Endometrial Hyperplasia
- Use of Estrogen for Menopausal Hormone Therapy
- Use of Tamoxifen to prevent or treat Breast Cancer
- No Child-Birth
- Start of Menstrual Period before the age of 12 yrs
- Occurrence of Menopause after the age of 55 yrs
- Family History of Uterine Cancer or Colorectal Cancer
Signs & Symptoms
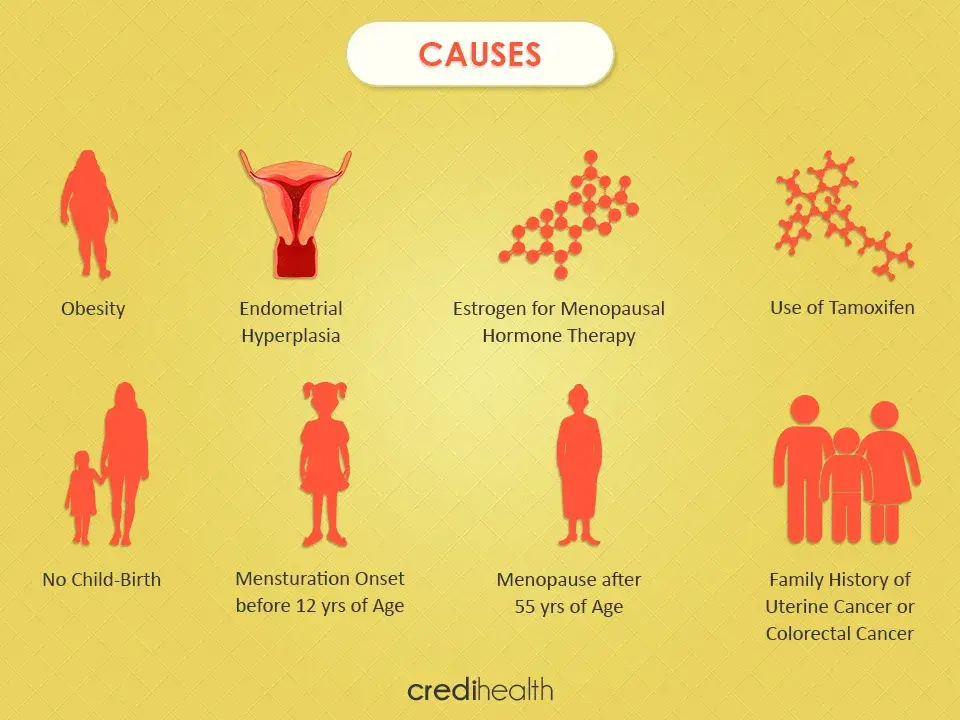
The common signs & symptoms of Uterine Cancer are as follows:
- Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding
- Pain in the Pelvic Area
- Abnormal Vaginal Spotting or Discharge
- Difficulty in Urinating
- Menstrual Irregularities, such as, Bleeding after Menopause, Periods lasting more than seven days, Bleeding between Periods, and Heavy Bleeding
- Pain during Sexual Intercourse
Specialists on Credihealth
For treatment and management of Uterine Cancer, one should consult a health care team consisting of Gynecologists, Gynecologic Oncologists, Medical Oncologists, and Radiation Oncologists.
Diagnosis
The doctor will carry out the following Diagnosis:
- History: People with a family history of Uterine Cancer and/or Colorectal Cancer are at an elevated risk for the disorder. Hence, the doctor will require information about patient's family history, symptoms, and overall health condition.
- Physical Examination: The doctor may conduct a physical examination of the patient's Uterus, Vagina, and nearby Tissues to check for any lumps or change in size.
- Tests: The doctor may conduct several tests, such as, Pap Test, Transvaginal Ultrasound, CT Scan, and MRI. The doctor may perform a Biopsy to check for Cancer Cells. If the doctor suspects that the Cancer has spread to the Lungs or other parts of the body, then he may recommend a Chest X-Ray or other relevant tests.
Treatment Modalities Available for Management of the Disorder
There is a host of options available for treatment of Uterine Cancer. However, the choice of treatment depends upon various factors, such as, Grade of the Tumor, Age & General Health of the patient, Spread of Tumor to other organs of the body, condition of the Muscle Layers of the Uterus, and condition of the Tissues outside the Uterus.
Surgery: Surgery is the most common treatment and may involve removal of Uterus, Cervix, Ovaries, Fallopian Tubes, nearby Lymph Nodes, and part of the Vagina. The surgery known as Hysterectomy may involve removal of organs, fully or partially. The choice of Surgery depends on the patient's wish and stage of the Cancer.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses Anti-Cancer drugs to destroy Cancer Cells. The doctor may recommend Chemotherapy after the Surgery to eliminate the risk of recurrence of Cancer.
Radiation Therapy: This form of therapy uses High-Energy Rays to kill Cancer Cells. It is of two types, namely, Internal Radiation Therapy and External Radiation Therapy. The doctor may recommend Radiation Therapy before or after the Surgery.
Hormone Therapy: Doctors may recommend Hormone Therapy in cases where Lab Tests reveal that the Uterine Tumor has Hormone Receptors. Patients with Stage 1 Cancer, who do not wish to opt for Surgery, may choose Hormone Therapy for treatment of Uterine Cancer.
Known Complications
Uterine Cancer may cause life-threatening situations. Cancer Cells from the Uterus may spread to other parts of the body, such as, Intestine, Lungs, Liver, Brain, or Bones. Post-Surgery, the patient shall not be able to bear children, and may experience other complications, such as, Hot Flashes, Nausea, Vomiting, Fatigue, Vaginal Dryness, Night Sweats, Swelling in Legs, and Loss of Sexual Intimacy.
Side Effects of Radiation Therapy include Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Urinary Problems, Hot Flashes, and some symptoms of Menopause. The patient may also experience Dryness, Itching, or Burning sensation in the Vagina. Patients undergoing Chemotherapy may experience complications, such as, Hair Loss, Poor Appetite, Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Mouth Sores, Lip Sores, Skin Rash, Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet, Hearing Problems, Loss of Balance, Joint Pain, and Swelling in Legs and Feet.
Precautions
Uterine Caner has high chances of recurrence. Hence, post treatment, one should keep a check on Cancer symptoms. The patient should take the following precautions and consult the doctor in the following eventualities:
- Excessive Bleeding from Vagina, Bladder, or Rectum
- Pain in the Abdomen or Pelvis
- Shortness of Breath or Cough
- Bloated Feeling
- Swollen Legs
Dietary and Physical Activity Requirements
During Cancer treatment, patients may feel weak or tired and may experience a loss of appetite. However, one should try to consume nutritious food with the right amount of calories and protein to maintain strength. Doctors recommend that patients undergoing Radiation Therapy should try to remain physically active.
Prevention of the Disorder from Happening or Recurring
One cannot prevent occurrence of Uterine Cancer, but may reduce the risk of the disorder. One should follow the below mentioned preventive measures:
- Regular physical exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Usage of Contraceptives
- Seek medical help if there is a family history of Uterine Cancer
Risk to other Family Members
Uterine Cancer is a Hereditary Illness and hence imposes a threat to other family members.
Support and Help given by the Caregiver
Patient suffering from Uterine Cancer may undergo stress and emotional turmoil. For patients who have undergone Surgery, it may create distressing situations, as the patient will no longer be able to bear children. In some cases, the treatment may also affect sexual intimacy. Under such circumstances, the partner should provide emotional support and allow the patient to share her feelings. The couple may seek help from a Counsellor.

Reviewed by